
#include <biosphere.h>Include dependency graph for copy.h:

This graph shows which files directly or indirectly include this file:

Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| bs_definition * | copy_definition (const bs_definition *def) |
| bs_service_request * | copy_request (const bs_service_request *req) |
| bs_service_response * | copy_response (const bs_service_response *resp) |
| void | delete_definition (bs_definition *def) |
| void | delete_request (bs_service_request *req) |
| void | delete_response (bs_service_response *resp) |
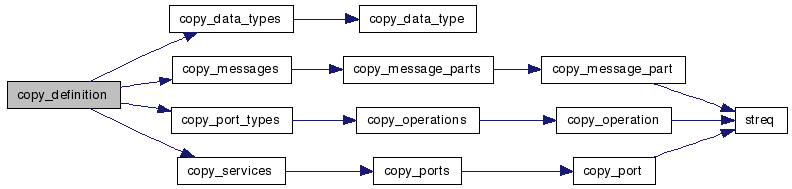
| bs_definition* copy_definition | ( | const bs_definition * | def | ) |
Create a deep copy of the given definition which is allocated using traditional memory allocation techniques.
| def | The bs_definition that is to be deep-copied |
Definition at line 274 of file copy.c.
References copy_data_types(), copy_messages(), copy_port_types(), copy_services(), and bs_definition::name.
Referenced by copy_bs_definition().
Here is the call graph for this function:
| bs_service_request* copy_request | ( | const bs_service_request * | req | ) |
Create a deep copy of the given request which is allocated using traditional memory allocation techniques.
| def | The bs_service_request that is to be deep-copied |
Definition at line 327 of file copy.c.
References copy_message_instance_data(), bs_service_request::input, bs_service_request::operation, bs_service_request::port, bs_service_request::service, and bs_service_request::uuid.
Here is the call graph for this function:

| bs_service_response* copy_response | ( | const bs_service_response * | resp | ) |
Create a deep copy of the given response which is allocated using traditional memory allocation techniques.
| def | The bs_service_response that is to be deep-copied |
Definition at line 354 of file copy.c.
References copy_message_instance_data(), bs_service_response::fault, bs_service_response::operation, bs_service_response::output, bs_service_response::port, bs_service_response::service, and bs_service_response::uuid.
Referenced by copy_bs_service_response(), and handle_service_request().
Here is the call graph for this function:

| void delete_definition | ( | bs_definition * | def | ) |
Free a malloced bs_definition by also freeing its internal structures. Make sure that the passed definition is allocated from a pool and not from a memory pool.
| def | The definition to be deleted |
Definition at line 464 of file copy.c.
References delete_data_types(), delete_messages(), delete_port_types(), delete_services(), bs_definition::from_mp, and bs_definition::name.
Referenced by delete_bs_definition().
Here is the call graph for this function:

| void delete_request | ( | bs_service_request * | req | ) |
Free a malloced bs_service_request by also freeing its internal structures. Make sure that the passed request is allocated from a pool and not from a memory pool.
| def | The definition to be deleted |
Definition at line 507 of file copy.c.
References delete_message_instance(), bs_service_request::from_mp, bs_service_request::input, bs_service_request::operation, bs_service_request::port, and bs_service_request::service.
Here is the call graph for this function:
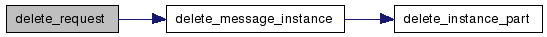
| void delete_response | ( | bs_service_response * | resp | ) |
Free a malloced bs_service_response by also freeing its internal structures. Make sure that the passed response is allocated from a pool and not from a memory pool.
| def | The definition to be deleted |
Definition at line 521 of file copy.c.
References delete_message_instance(), bs_service_response::fault, bs_service_response::from_mp, bs_service_response::operation, bs_service_response::output, bs_service_response::port, and bs_service_response::service.
Referenced by handle_http_post().
Here is the call graph for this function:

 1.5.1
1.5.1