
|
Collaboration diagram for Module Subsystem:

|
Data Structures | |
| struct | module_info |
Defines | |
| #define | module_is_loaded(m) (get_module_info(m) != NULL) |
Functions | |
| bs_status | load_module (const char *name) |
| bs_status | unload_module (const char *name) |
| bs_status | unload_all_modules (void) |
| bs_status | init_module (apr_pool_t *mp) |
| bs_module * | get_module_info (const char *name) |
| bs_status | get_module_descriptions (bs_list *names, bs_list *fnames, bs_list *versions, bs_list *descriptions) |
| #define module_is_loaded | ( | m | ) | (get_module_info(m) != NULL) |
Checks if the named module is loaded.
| name | Name of the module |
Definition at line 113 of file module.h.
Referenced by load_module().
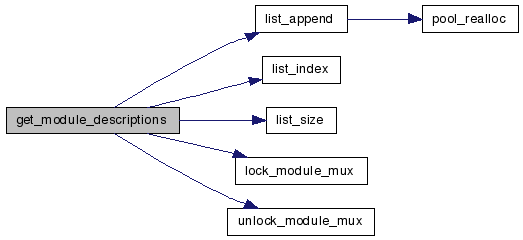
| bs_status get_module_descriptions | ( | bs_list * | names, | |
| bs_list * | fnames, | |||
| bs_list * | versions, | |||
| bs_list * | descriptions | |||
| ) |
Fill the two provided lists with the modules names and their corresponding descriptions. The strings are allocated from the pools provided in the two lists.
| names | The list that will be filled with all the loaded module names | |
| descriptions | Descriptions of all the loaded modules |
Definition at line 264 of file module.c.
References BS_OK, module_info::def, bs_module::description, list_append(), list_index(), list_size(), lock_module_mux(), bs_module::module_major, bs_module::module_minor, modules, bs_module::name, module_info::name, bs_list::pool, and unlock_module_mux().
Referenced by core_service_module_service_list().
Here is the call graph for this function:
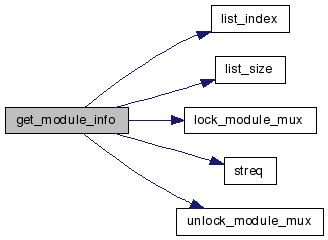
| bs_module* get_module_info | ( | const char * | name | ) |
Return the structure that describes the module.
| name | Name of the module |
Definition at line 245 of file module.c.
References list_index(), list_size(), lock_module_mux(), modules, streq(), and unlock_module_mux().
Referenced by main().
Here is the call graph for this function:
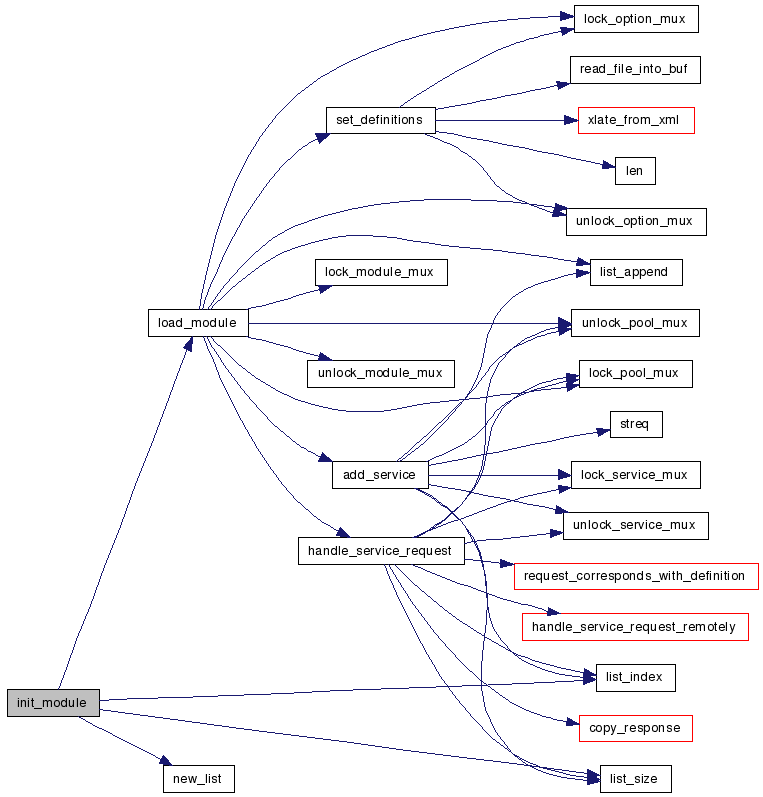
| bs_status init_module | ( | apr_pool_t * | mp | ) |
Initialize the module manager subsystem.
Definition at line 232 of file module.c.
References BS_ERROR, BS_OK, global_module_names_list, list_index(), list_size(), load_module(), modules, and new_list().
Referenced by main().
Here is the call graph for this function:
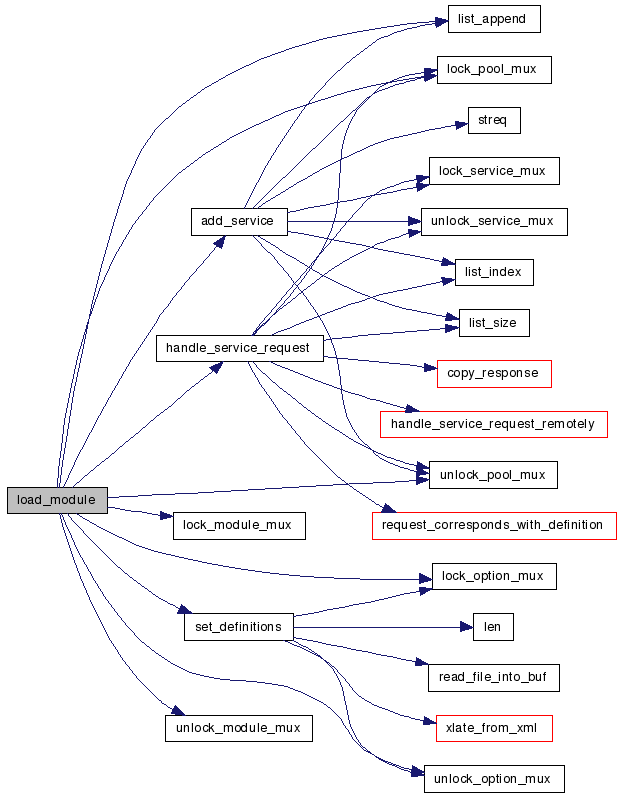
| bs_status load_module | ( | const char * | name | ) |
Load the named module. We need the global memory pool, since the modules are meant to persist after the thread (and its mem. pool) have died. The function must also be thread safe.
| name | Name/path of the module to load |
Definition at line 95 of file module.c.
References add_service(), BIOSPHERED_MODULES_DIR, BS_ERROR, BS_OK, module_info::def, global_modules_dir, global_mp, handle_service_request(), bs_module::handler, bs_module::init, list_append(), lock_module_mux(), lock_option_mux(), lock_pool_mux(), module_info::modh, module_is_loaded, modules, bs_module::name, module_info::name, runtestsuite::rv, module_info::services, set_definitions(), bs_module::syshandler, module_info::time_loaded, unlock_module_mux(), unlock_option_mux(), and unlock_pool_mux().
Referenced by core_service_module_service_load(), init_module(), and main().
Here is the call graph for this function:
| bs_status unload_all_modules | ( | void | ) |
Unload all modules. This can be used at exit time.
Definition at line 208 of file module.c.
References BS_OK, bs_module::cleanup, module_info::def, list_index(), list_remove(), list_size(), lock_module_mux(), module_info::modh, modules, module_info::name, bs_definition::name, remove_service(), runtestsuite::rv, module_info::services, and unlock_module_mux().
Referenced by shutdown_thread_main().
Here is the call graph for this function:
| bs_status unload_module | ( | const char * | name | ) |
Unload the named module.
| name | of the module to unload. |
Definition at line 176 of file module.c.
References BS_ERROR, BS_OK, list_index(), list_remove(), list_size(), lock_module_mux(), modules, remove_service(), runtestsuite::rv, streq(), and unlock_module_mux().
Referenced by core_service_module_service_unload(), and main().
Here is the call graph for this function:
 1.5.1
1.5.1